
A Simple Sector Syntax
Here are some key takeaways:
Sector classifications in the Voluntary Carbon Market are inconsistent and confusing. We find 94 defined sectors across the five major accreditors.
BeZero’s Carbon Sector Classification System simplifies the market into three levels: six sector groups, fourteen sectors and forty two sub-sectors.
Mapping BeZero Carbon Ratings coverage by sector to the wider VCM reveals a bias to Nature Based Solutions and Tech Removals.
Contents
- A lack of standardisation is confusing the market
- A new syntax for carbon sectors
- Mapping BeZero Carbon Ratings sector coverage to the wider VCM
Please note we updated our Sector Classification System in July 2023. Learn more here.
A lack of standardisation is confusing the market
Analysis of the major five accreditors reveals a combined total of 94 defined sectors. Inconsistencies across global registries include: the number and names of sectors covered; the downstream labelling of projects; their sub-sectors or identification as whether they are removal or reduction credits.
Discrepancies also add considerable complexities. The feedback we’ve received is that participants find it difficult to compare projects on a like-for-like basis; to know what’s driving the project’s primary avoidance or removal activity; to create accurate sectoral analysis; to perform portfolio analysis.
The market needs a simplified sector syntax analogous to traditional financial markets, such as MSCI’s Global Industry Classification Standard. So we built one.
A new syntax for carbon sectors
The BeZero Carbon Sector Classification System is a hierarchical sector classification system for the Voluntary Carbon Market (VCM) comprising three tiers; sector group, sector and sub-sector.
VCM projects are classified based on a quantitative and qualitative assessment. Each project is assigned a single classification at the sub-sector level based on the primary activity undertaken by the project. Thematic consistency and market perceptions are also considered for classification purposes. Consistent meta-data labels play a key role in market efficiency.
BeZero has developed a three tier view to consolidate the makeup of the current market — see Table 1. Our data driven approach appropriately labels projects according to what a majority of their issuance activities contribute to.
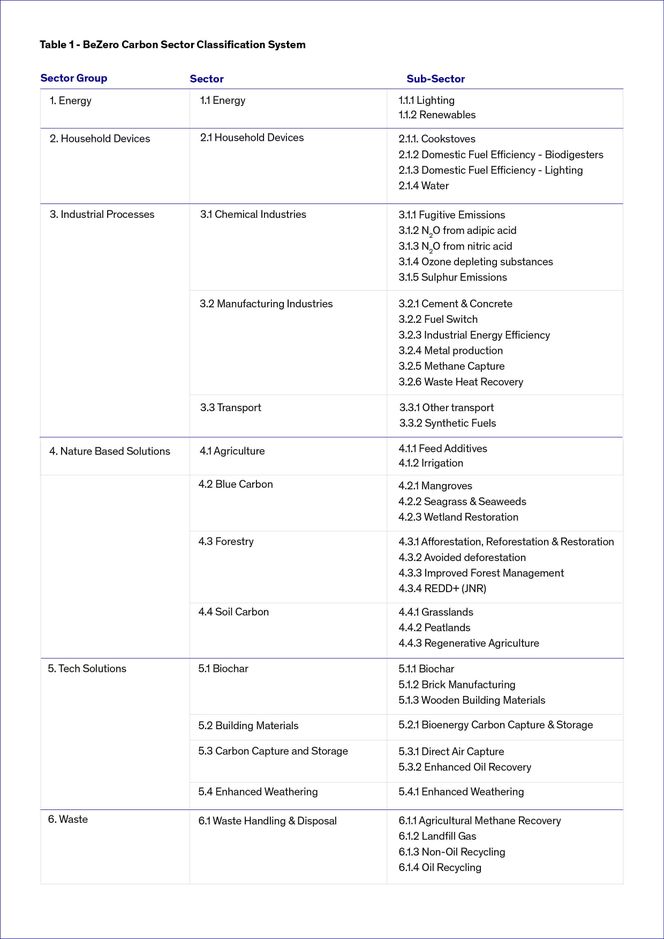
BeZero Carbon Sector Classification System in detail.
The BeZero sector classification includes a number of distinct groupings not found in other market classification systems to reflect projects with distinctive features such as common ecosystems or technologies. Some notable examples include the following:
Peatlands is a stand-alone subsector within Soil Carbon and Nature Based Solutions. Typically, many of the large peatlands projects follow REDD+ methodologies and are classified as such by many organisations. However, we believe that the unique ecological characteristics of peatlands — notably large below ground carbon pools — warrant a separate classification.
The Grasslands sub-sector includes project activities leading to increased carbon stocks in grasslands including both wild and in farmed landscapes. Rotational grazing and other regenerative livestock farming practices are common features particularly for the latter.
Regenerative Agriculture therefore tends to include arable farming related activities aimed at soil organic carbon (SOC) sequestration. These include reductions in tillage and fertiliser application among other potential activities.
Blue Carbon is a separate sector reflecting the growing interest in blue carbon as a Nature Based Solution and the emerging pipeline of VCM projects. We have 3 sub-sectors within Blue Carbon, one each for Mangroves, Seagrass & Seaweeds, and Wetland Restoration. Note that Mangroves projects could involve either REDD+ or ARR activities, or both.
The Tech Solutions sector group is geared to the emerging carbon removal sector linked to new and innovative technologies. These include technologies used purely for carbon removals such as Direct Air Capture, in the Building Materials sector, or downstream in agriculture such as Biochar.
In certain instances, various project activities have been condensed to single sub-sectors. For example, the sub-sector ‘Other Transport’ includes projects related to a range of activities including electric vehicles, fleet efficiency, and mass transit. Such examples occur when activity types contribute to a small fraction of the VCM’s overall issuance.
Mapping BeZero Carbon Ratings sector coverage to the wider VCM
BeZero coverage is designed to be as close to the wider VCM as possible, and takes a large-cap first approach, i.e. we target the biggest ratable projects by total credits outstanding.
The 184 BeZero rated projects on our platform today are on average 14 times larger than the typical VCM project (1.76 million credits outstanding vs. 129k across the VCM universe). BeZero’s coverage also represents ~40% total credits outstanding within the defined VCM**, including projects in each of the 6 Sector Groups, and 12 of 14 Sectors.
Chart 1 shows that our rated universe does have a moderate sector bias in terms of credits outstanding. Our coverage today is overweight Nature Based Solutions, and Technology Solutions but shows a small underweight in Household Devices, Energy, and Industrial processes.

This chart compares the share of credits outstanding for BeZero rated projects (184) compared to total VCM by Sector Group as defined by BeZero Carbon Sector Classification System.
The clearest trend is that Nature Based Solutions dominate the VCM. Within that Forestry is by far the largest single sector, representing 45% of the VCM and 51% of BeZero’s coverage by credits outstanding. The other emerging sector is Soil Carbon, which accounts for 6% of credits outstanding and 12.8% for BeZero’s coverage. The Peatlands sub-sector accounts for the vast majority of available volume currently. Vintage analysis helps justify our pro-Nature coverage bias. Assessing total credits outstanding since 2016 reveals NBS projects are on the rise (from 52% to 56%) with waste projects falling the most (from 5% to 3%).
Chart 2 shows the BeZero rated universe versus the VCM in terms of number of projects. It reveals BeZero’s coverage has a higher concentration of Nature Based Solutions & Technology Solutions projects versus a lower concentration of Household Devices and Energy projects.

This chart compares the total number of BeZero rated projects (184) compared to total VCM by Sector Group as defined by BeZero Carbon Sector Classification System.
A comparison of Charts 1 and 2 also reveals a low correlation across the market between credits outstanding and total projects.
For example, Energy (37%) and Nature Based Solutions (15%) projects account for 52% of total VCM projects vs. a combined 81% in volume terms (Energy — 29%, Nature Based Solutions — 52%). By comparison, Household Devices projects account for 24% of projects but just 4% of credits outstanding in the VCM.
Chart 3 shows BeZero’s sector bias by number of projects at the Sub-Sector level. The key areas of divergence lie in the low coverage of Agricultural Methane Recovery, Water, and Ozone Depleting Substances and higher coverage of forestry sub-sectors, e.g. Avoided Deforestation and Afforestation, Reforestation & Restoration.

**Note: the VCM market statistics above include projects listed by four major voluntary offset project registries — Verra (VCS), Gold Standard, Climate Action Reserve (CAR), and American Carbon Registry (ACR). Projects registered under the UN’s Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) have been excluded.